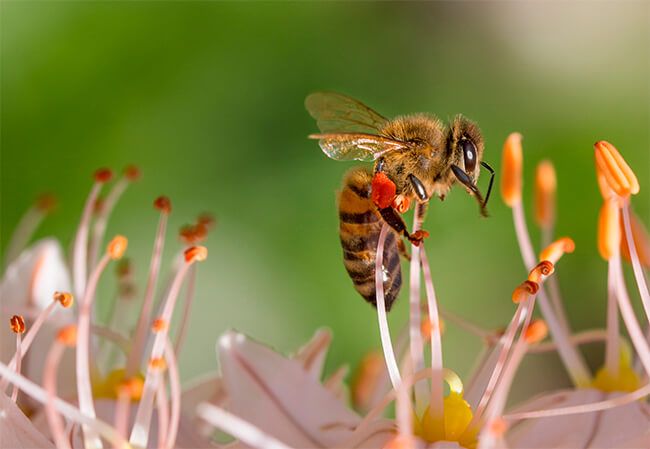
Beekeepers and farmers ─ communication is key to protect bees
- One third of food crops in the world depend on pollination.
- Dialogue and collaboration between farmers and beekeepers will contribute to the health of bees.

2018
Encouraging dialogue and collaboration between farmers and beekeepers should be a constant task to achieve the protection of bees, the coexistence and mutual benefit of the two activities.
These insects are threatened by viruses, bacteria, other insects, climate change, nutritional failures, decreased habitats and poor beekeeping and agricultural practices. For José Perdomo, president of CropLife Latin America, it is important that farmers and beekeepers implement good beekeeping and agricultural practices, communicate constantly and have a sense of mutual collaboration. In the end, these practices will result in the coexistence of the two activities and the protection of bees and pollinators.
It is important that beekeepers know the crops near their hives - not further than 1 kilometer - as they are a source of food for bees. Provide feeding areas with pollen and nectar and routinely inspect hives to control diseases and mite infestations such as Varroa, which is the leading cause of bee deaths worldwide.
Likewise, it is recommended that farmers take into account that pollinators should be identified from the territory where the crop is located, that they know foraging habits and promote safe spraying practices, so as not to affect pollinators. Also, they ought to implement the planting of flowering plants near the crop, which can increase 30% of productivity thanks to good pollination.
CropLife Latin America is committed to the protection of bees and seeks to encourage dialogue between beekeepers and farmers through educational materials, including the video "Farmers and Beekeepers, united by the health of pollinators.” Available Here
Join the protection of bees as an agriculture initiative and follow these recommendations:
- Improve the habitat of pollinators by planting beds of flowers and keeping rows at the edges and spaces without applications.
- Implement an integrated pest management plan to apply pesticides only when necessary.
- Inform local beekeepers in advance before applications, so that nearby hives can be moved or protected.
- Use only genuine products and alert your authorities regarding adulterated or illegal products that have unknown impacts on wildlife.
- Follow the instructions on the label to use the correct dosage. Avoid applying products during windy conditions, in order to prevent spillage or powder drift.
- Use reduced drift application equipment that is well maintained and calibrated.
- Avoid contamination of sprays during mixing and properly dispose of waste and other materials used.
- Avoid pesticide applications when the bees are foraging and when the plants are in bloom.
- Minimize the carefully treated seed powders drift by emptying it from the bags. Use sowing machinery that eliminates dust production and keeps the equipment regularly clean.